Periodic Assessment
The English user guide is currently in beta preview. Most of the documents have been automatically translated from the Japanese version. Should you find any inaccuracies, please reach out to Flatt Security.
What is Periodic Assessment?
Takumi can periodically assess repositories linked to Slack channels.
When you enable periodic assessment in the Active Takumi settings, Takumi will review commit differences within the specified period and notify the results to your Slack channel.
Recommended Usage
Periodic assessments help you regularly visualize the latest security risks even in teams where features are frequently added or modified.
We particularly recommend running assessments at these times:
- Run assessments on weekends and share the latest issues at Monday morning team meetings
- Set assessments the day before regular meetings to review each development cycle
Difference from Scheduled Tasks
A similar feature to periodic assessment is Scheduled Tasks.
- Scheduled Tasks: You can freely request any task from Takumi at any timing.
- Periodic Assessment: Specialized for performing regular reviews targeting commit differences within a specified period. Since it targets differences, it tends to consume fewer credits than assessing the entire application.
While scheduled tasks offer high flexibility, depending on the request content, there may be variations in assessment accuracy. With periodic assessments, we manage the prompts on our side and provide workflows optimized for this workload, achieving stabilization and efficiency in assessment accuracy.
If you want to regularly assess the entire application instead of commit differences within a period, please use Scheduled Tasks.
When changing an already configured scheduled task to a periodic assessment, you need to set up the periodic assessment and delete the scheduled task. When deleting the scheduled task, if it was set up on Slack, it needs to be deleted from Slack, and if it was set up on Shisho Cloud byGMO, it needs to be deleted from Shisho Cloud byGMO.
Expected Review Time
It may take approximately 4 to 8 hours from when Takumi starts the assessment until completion.
How to Set Up Periodic Assessments
-
Invite Takumi to your Slack and set the required scopes. For details, see Invite Takumi to Slack.
-
Enable periodic assessment from "Settings > Takumi" in the Active Takumi settings.
You can choose the report frequency as "weekly" or "monthly". Takumi will perform a security review on the commit differences within the specified period.
Periodic Assessment Usage Example
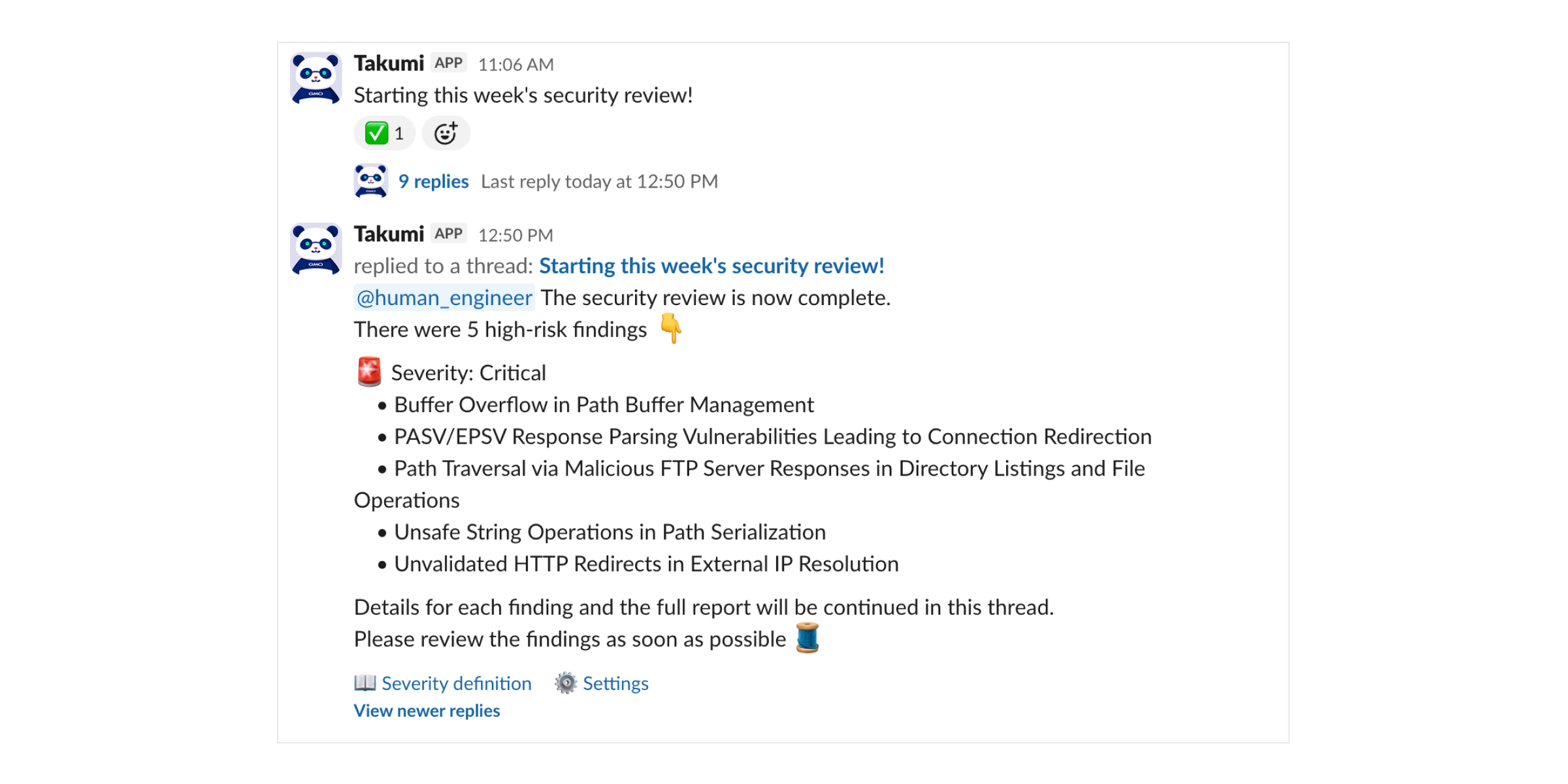
When periodic assessment is enabled, you will receive results on Slack in the following format.
Slack Notification Example
Outputting the assessment report in Markdown format
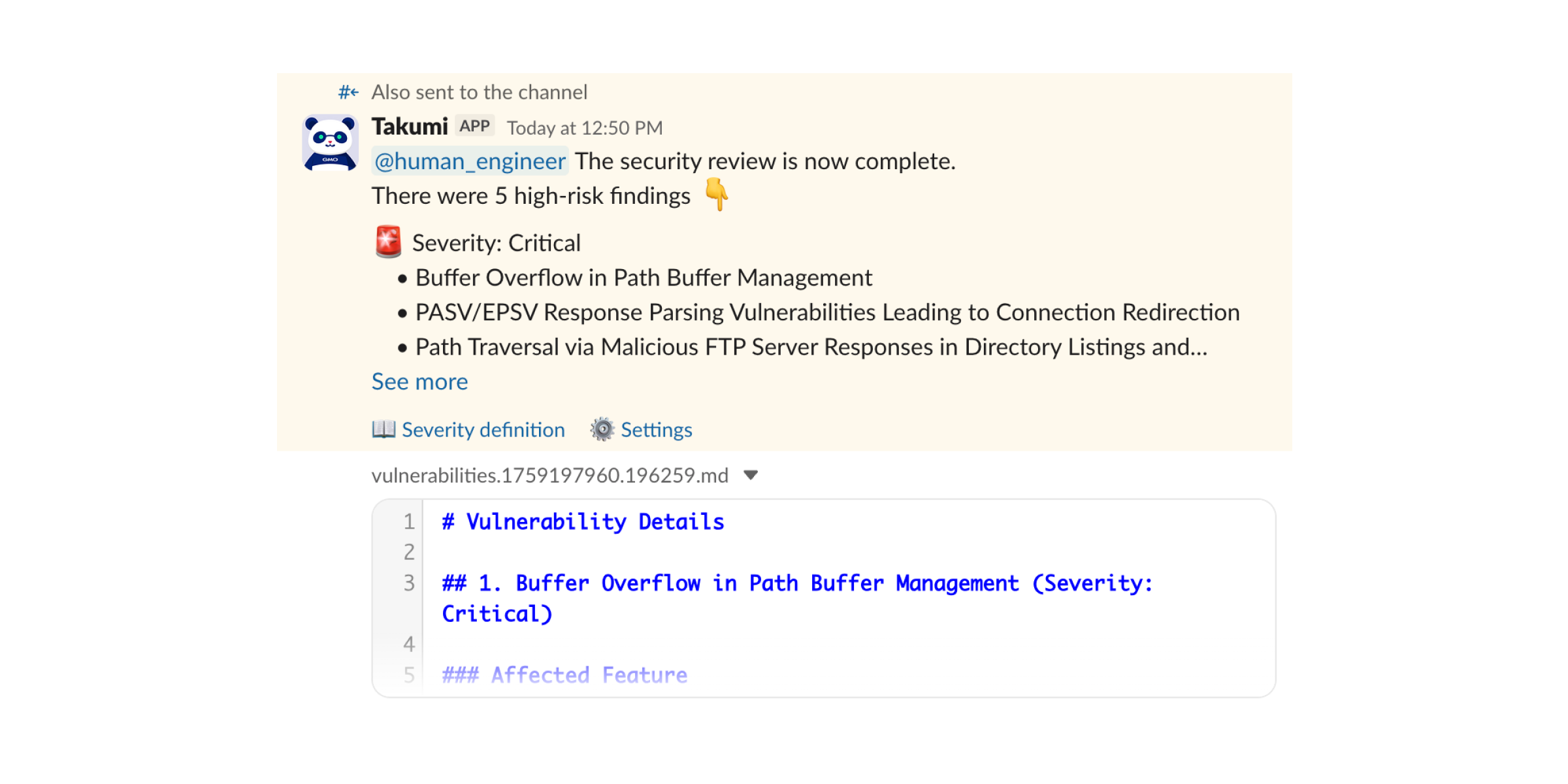
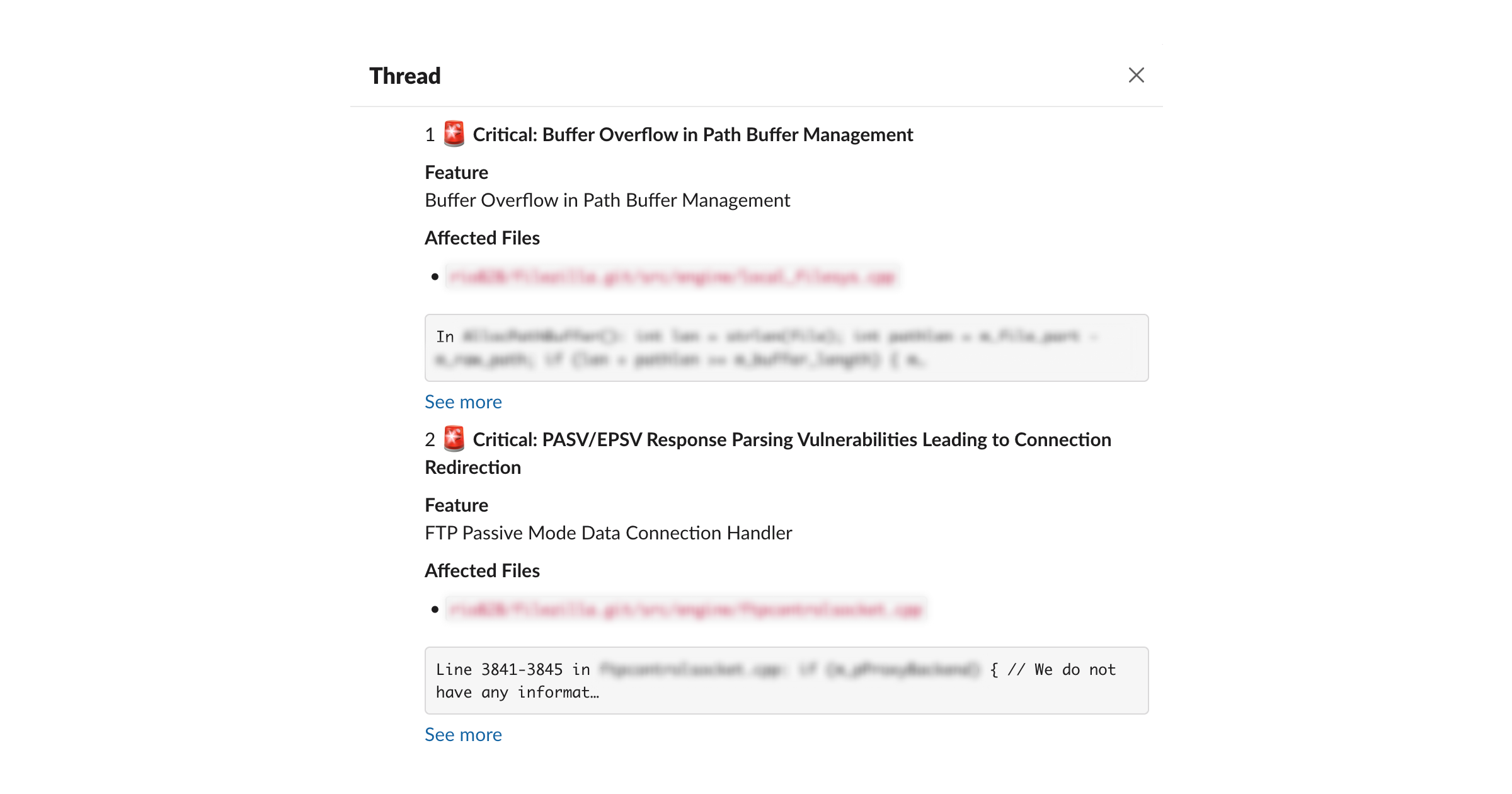
Explaining high-risk findings in threads
Markdown Output Example
# Vulnerability Details
## 1. FTP PASV Response Injection and SSRF via Malicious Passive Mode Response (Severity: Critical)
### Affected Feature
FTP Passive Mode Processing
### Impacted Code
- src/network/ftp.cpp
- src/network/ftp.h
In ftpsocket.cpp line 182: host = regex.GetMatch(m_Response, 2); followed by lines 183-183 for port extraction, then line 125: socket->SetupConn(host, port) connects to attacker-controlled destination
### Description
The ProcessResponse function in the FTP control socket parses PASV responses using regular expressions, but validation is insufficient. A malicious FTP server can return a crafted PASV response containing arbitrary IP addresses and ports, potentially causing SSRF attacks where the client connects to internal network resources. The regular expression pattern allows values of 0-999 for IP octets (exceeding the valid 0-255 range) and does not validate port ranges, allowing attackers to redirect data connections to any host and port including localhost, internal IPs, or restricted services.
### Risk
The primary risk of this vulnerability is that attackers can perform unauthorized access to internal network services or services on localhost. This can lead to theft of sensitive information from internal systems, unauthorized access to internal services, or bypassing firewalls and other security controls. In particular, databases, administrative interfaces, and other sensitive systems on the organization's internal network may be at risk.
### Solution
The most important fix for this vulnerability is to strengthen input validation in PASV response parsing. Specifically, you need to verify that each octet of the IP address is within the valid range of 0-255, and that the port number is within the valid range of 1-65535. Additionally, implement comprehensive whitelist validation for destination IP addresses, and explicitly block connections to private IP addresses, localhost, and internal networks. It is also recommended to restrict configurations to connect only to trusted FTP servers.