Web Application Security Assessment
The English user guide is currently in beta preview. Most of the documents have been automatically translated from the Japanese version. Should you find any inaccuracies, please reach out to Flatt Security.
How It Works
Shisho Cloud sends simulated attacks to detect vulnerabilities by examining the responses. This is done against each registered Scenario, which is a sequence of dependent Endpoints.
Some applications require specific information, such as authentication headers or cookies, to be included in the request after login. You can specify these headers by registering Authentication Settings. These settings will include the headers when sending requests during crawling and assessment. Values for headers can be specified as fixed values or extracted dynamically by replaying scenarios representing login operations.
In some cases, you may want to exclude certain parts of your application from the assessment. You can assess only specific parts of your application by configuring the Scope.
The following sections describe each concept in more detail.
Scope
Scope defines which parts of the application will be assessed.
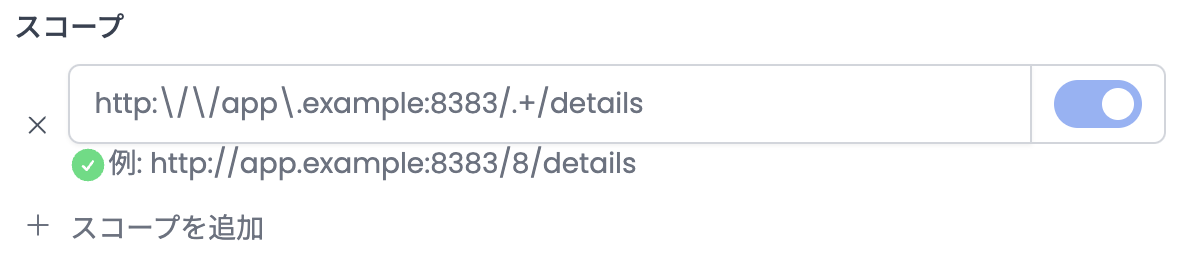
In the default input mode, you can specify a URL prefix. URLs starting with that prefix will be assessed. You can specify multiple prefixes by clicking the "Add Scope" button.

You can define the scope using regular expressions instead of prefixes by switching to advanced mode using the toggle.
Scenario
A Scenario is a unit of assessment represented by a sequence of dependent endpoints. For example, the following request flow can be expressed as a Scenario. This enables assessment based on endpoint relationships.
- Extract the CSRF token from the input screen and include it in a POST request.
- Send a request to create an item before sending a request to delete an item.
- After sending a request to create an item, send a request for the screen that displays the item information to detect vulnerabilities in accumulation.
A Scenario consists of one or more Steps. Each step refers to an endpoint that sends a request.
For example, the following two-step Scenario requests the item list screen after an item is created. This detects cumulative vulnerabilities caused by item creation.

The YAML input field for each step can contain the following options.
- Define the input/output relationship between steps
extractors: Extracts values from request results, stores those values in variables, and makes them usable in subsequent steps.bindings: Injects the values stored in variables byextractorsin previous steps into the request parameters of the current step.
- Adjust handling during assessment
skipInjection: Do not inject attack payloads into the step.

extractors
This setting extracts values from request results, stores those values in variables, and makes them available in subsequent steps. It specifies an array of Extractor Objects. You can extract multiple pieces of information and store them in variables by specifying multiple Extractor Objects as array elements.
For example, if you enter the following in the YAML input field, the response body will be matched against the regular expression token=([a-z0-9]+). The portion matching ([a-z0-9]+) will be stored in the variable token.
extractors:
- name: token
type: regex
regex:
- "token=([a-z0-9]+)"
group: 1
Extractor Object
An Extractor Object defines how to extract a value from the result of a request and the variable name to store the extracted value.
The basic structure is as follows. bindings in subsequent steps uses the variable name specified by name. Specify the type of extraction method in type. This is followed by configuration items for each extraction method.
name: "<Variable name to store>"
type: "<Extraction method type>"
# ... <Settings according to the extraction method> ...
The extraction method type is one of the following:
regex: Extracts values from strings using regular expressionsxpath: Extracts values from HTML/XML using XPathjson: Extracts values from JSON using jq queriescookie: Extracts all cookies from the response
regex Extractor
This Extractor represents extraction using regular expressions.
Configuration items:
regex: An array of regular expressions used for extraction- Refer to the RE2 documentation for syntax.
group: The number of the capture group from which to extract the value- Default: 0 (entire match)
part: The target to match with the regular expressionbody: The body of the response (default)header: The header of the responseall: Entire response
For example, the following Extractor matches the response header and stores the value portion of the Location header in a variable called redirect_url. This is the first group.
name: redirect_url
type: regex
regex:
- "(?m)^Location: (.+?)$\n"
group: 1
part: header
xpath Extractor
This Extractor uses XPath to extract values from HTML and XML.
Configuration items:
xpath: Array of XPath used for extractionattribute: Attribute name to extract- If not specified: Node text
For example, the following Extractor will search for an element like <input name="csrf_token" value="..."> inside the first <form> element. It then stores the value of its value attribute in a variable called csrf_token.
name: csrf_token
type: xpath
xpath:
- '(//form)[1]//input[@name="csrf_token"]'
attribute: value
You can obtain the XPath to the desired element using the browser's developer tools (https://devtoolstips.org/tips/en/copy-element-xpath/). The detailed procedure will vary depending on the browser. However, you can copy the XPath pointing to the element by right-clicking on the target element in the developer tools and selecting "Copy XPath". You can also check the XPath search results in the developer tools console. This can be done with the $x function (e.g., $x('//form[1]//input[@name="csrf_token"]')).
json Extractor
This Extractor uses jq queries to extract values from JSON.
Configuration item:
json: An array of jq queries used for extraction
For example, the following Extractor extracts the XXXX part and stores it in a variable called item_id if the response body is similar to {"item": {"id": "XXXX", ...}}.
type: json
name: item_id
json:
- ".item.id"
cookie Extractor
This Extractor extracts all cookies from the response.
Configuration item:
- None
For example, the following Extractor will search the response header for a string like Set-Cookie: key=value. It then stores the string with all the key=value pairs concatenated with ; in a variable called cookies.
type: cookie
name: cookies
bindings
This setting injects the values stored in variables by extractors in previous steps into the request parameters of the current step.
For example, the following configuration injects the CSRF token stored in a variable called csrf_token in the previous step into the .csrf_token parameter in the request body.
bindings:
- type: body # Type of parameter to inject
key: .csrf_token # Injection destination
extractorName: csrf_token # Variable name storing the value to be injected
type is one of pathParam, header, query, or body.
key specifies the parameter for injection.
- If the type is
pathParam,header, orquery, specify the parameter name as is (e.g., specifykey: 'Custom-Header'to inject into the headerCustom-Header: XXXX). - If the type is
body, specify the property name for injection by connecting property names with dots (e.g., if the request body is JSON like{"item": {"id": "XXXX", ...}}, specifykey: '.item.id'to inject the value into theXXXXportion).
extractorName specifies the variable name written in the name field in extractors in the previous step.
skipInjection
If you set skipInjection: true in a step, attack payloads will not be injected into that step during the assessment. For example, to detect a cumulative vulnerability, you might want to send an attack request to POST /items/new in the first step and then request GET /items in the second step. This checks if there is a problem with the response. You only need to inject the attack payload in the first step, so set skipInjection: true in the second step.
Authentication Settings
You can configure appropriate headers and cookies to be added to requests during crawling and assessment by defining authentication settings.
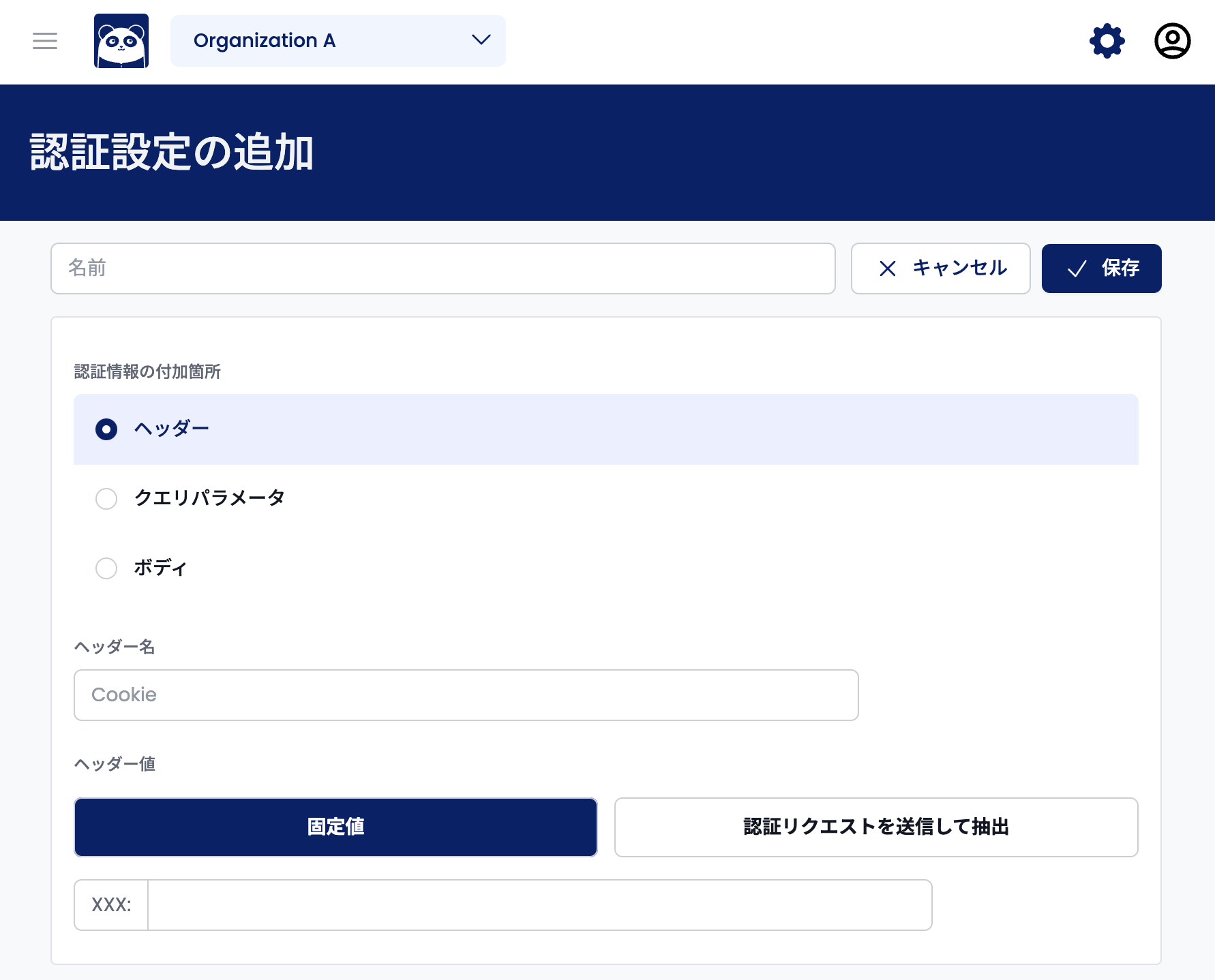
"Where to add authentication information" refers to where in the request you want to add information. The options are "Header", "Query Parameter", and "Body." For example, select "Header" and enter Cookie in the "Header Name" field to add a cookie.
You can specify the value you want to add to the request in the "Header Value" or "Parameter Value" field. There are two ways to specify the value: "Fixed Value" and "Send authentication request and extract." Use "Fixed Value" if the value does not have an expiration date. Use "Send authentication request and extract" if it does.
Enter the exact value you want to include in the request if you select "Fixed value."
Extracting Authentication Information from a Scenario
The following settings will appear when you select "Send authentication request and extract":
- "Authentication Information Acquisition Method": Keep it as "Extract from scenario." This indicates the scenario is used to obtain authentication information.
- "Authentication Request Scenario": A Scenario that represents the request procedure to get the desired value
- "Authentication Request Parameters": Parameters to inject into the above scenario (e.g., user name and password)
- "Authentication Information Extraction Method": How to extract the value from the response
- "Authentication Information Update Condition": Condition to resend the authentication request and extract it again (e.g., expiration date)
![Example of Entering "Send Authentication Request and Extract"]](../../../../i18n/ja/docusaurus-plugin-content-docs/current/concepts/web-application/images/precondition-create-dynamic.png)
Authentication Request Parameters
Specify the parameters to be injected into the "Authentication Request Scenario."
For example, the following configuration injects two parameters (username and password) into the first step (0-indexed) of the scenario.
- stepIndex: 1
type: body
key: .username
value: test
- stepIndex: 1
type: body
key: .password
value: n}0b6P@5jkjy&7<KFdwANh9f>IY_?,Ty
This setting requires an array of objects. Each object has the following properties.
stepIndex: The index of the step to inject the parameter into (0-indexed)type: Parameter type (pathParam,header,query, orbody)key: Parameter name- Specify the parameter name as is if the type is
pathParam,header, orquery. - If the type is
body, connect property names with dots to specify the property name (e.g., if the request body is JSON like{"item": {"id": "XXXX", ...}}, specifykey: '.item.id'to inject the value into theXXXXportion).
- Specify the parameter name as is if the type is
value: Parameter value
Authentication Information Extraction Method
Use the Extractor Object to specify how to extract the value from the response of the "Authentication Request Scenario." You can omit the Extractor's name field.
For example, the following setting will search the response header for a string like Set-Cookie: session=XXXX and extract the XXXX portion.
part: header
type: regex
regex:
- "Set-Cookie: (session=[a-zA-Z0-9]+)"
group: 1
Authentication Information Update Condition
Set the conditions to resend the authentication request and extract it.
For example, the following configuration will send and extract the authentication request when Shisho Cloud crawls or assesses the website or 60 minutes have passed since the last extraction.
- type: BLANK # Update in the initial state
config: {}
- type: EXPIRE # Update if more than 60 minutes have passed since the last extraction
config:
expiresIn: 60m
Each element in the array has a type field and a config field.
Specify one of the following for the type field:
BLANK: Update at initializationEXPIRE: Update when a certain period has passed since the last update
type: BLANK
The config field is an empty object {}.
type: EXPIRE
The config field specifies the expiration date that necessitates an update in the expiresIn field.
- type: EXPIRE
config:
expiresIn: 60m
Use s (seconds), m (minutes), or h (hours) for the expiresIn field's units.
Extracting Authentication Information from Prepared Authentication Processing
You can obtain authentication information using Shisho Cloud's prepared authentication processing. The following authentication processing is currently supported:
Go to "Authentication Information Acquisition Method" and select "Extract from prepared authentication processing." The settings for the specified authentication processing will appear.
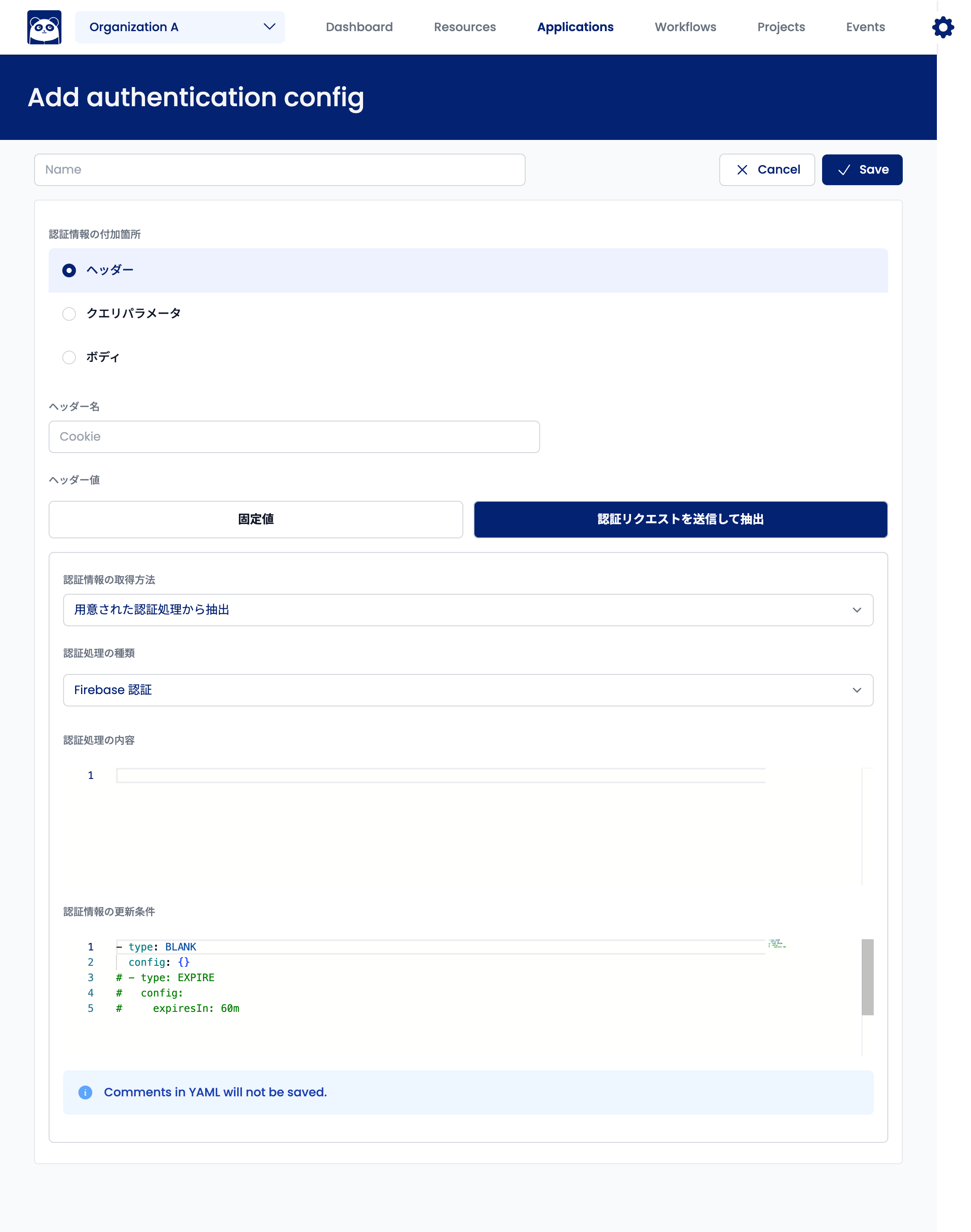
Extracting Authentication Information from Firebase Authentication
This authentication process connects to Firebase Authentication to obtain ID tokens. Currently, only email and password authentication is supported.
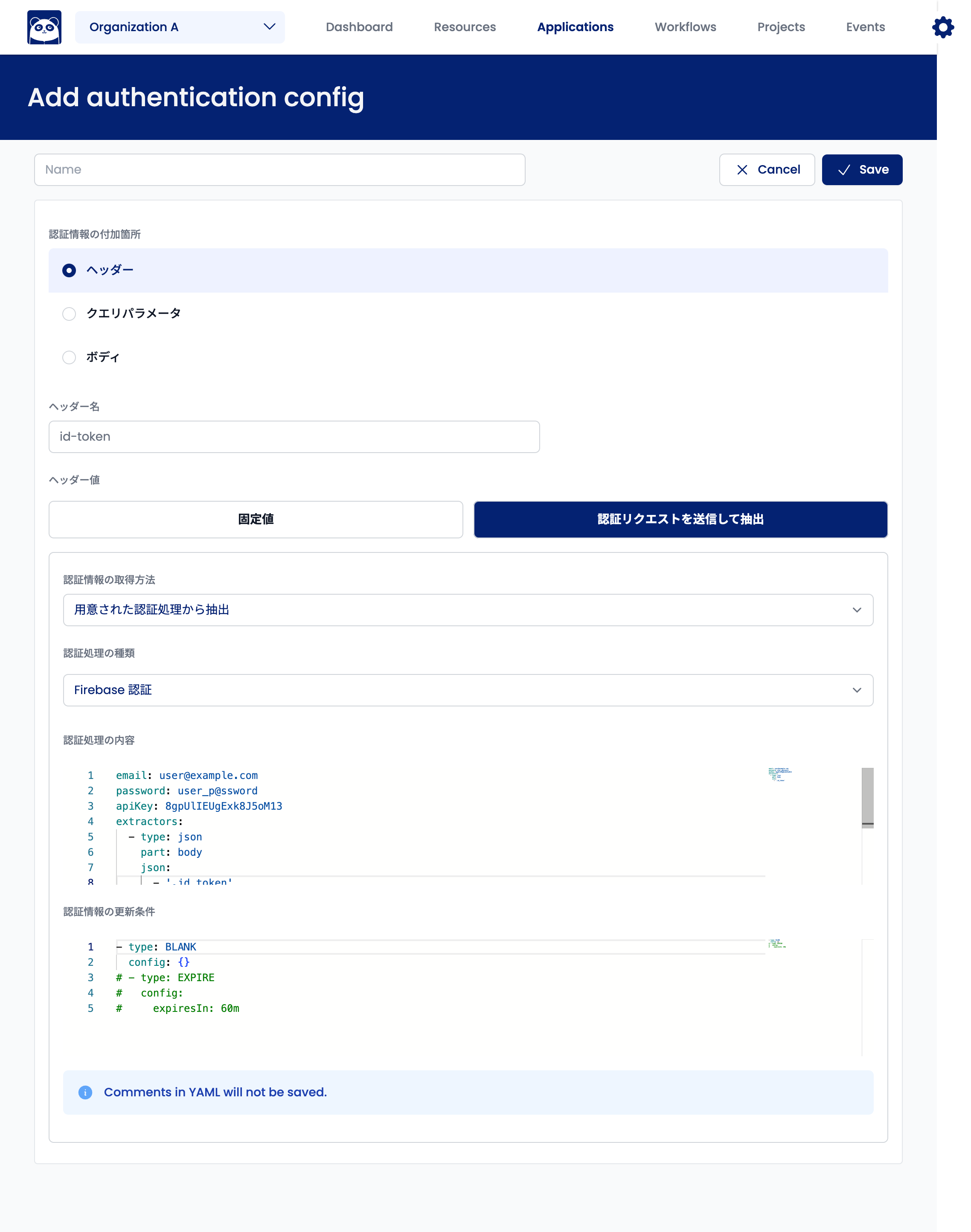
Select "Extract from Prepared Authentication Processing" for "Authentication Information Acquisition Method." Select "Firebase Authentication" for "Type of Authentication Processing."
The following fields are required for "Authentication Processing Details":
email: Login account's email addresspassword: Login passwordapiKey: API key issued by Firebase Authenticationextractors: Items of authentication information to extract
Example of "Authentication Processing Details":
email: user@example.com
password: user_p@ssword
apiKey: 8gpUlIEUgExk8J5oM13
extractors:
- type: json
part: body
json:
- ".id_token"
Specify json for type and body for part in extractors. You can specify the following values for the json field:
.id_token.refresh_token.expires_in
You can only specify one value for the json field. You can only specify multiple extractors if a scenario follows the current one as post-processing. If there is no scenario for post-processing, Shisho Cloud will extract the value set in extractors.
The "Authentication Information Update Condition" setting is the same as when extracting authentication information from a scenario.
Extracting Authentication Information from Cognito
This authentication process connects to Cognito to obtain ID tokens. Currently, only email and password authentication is supported.
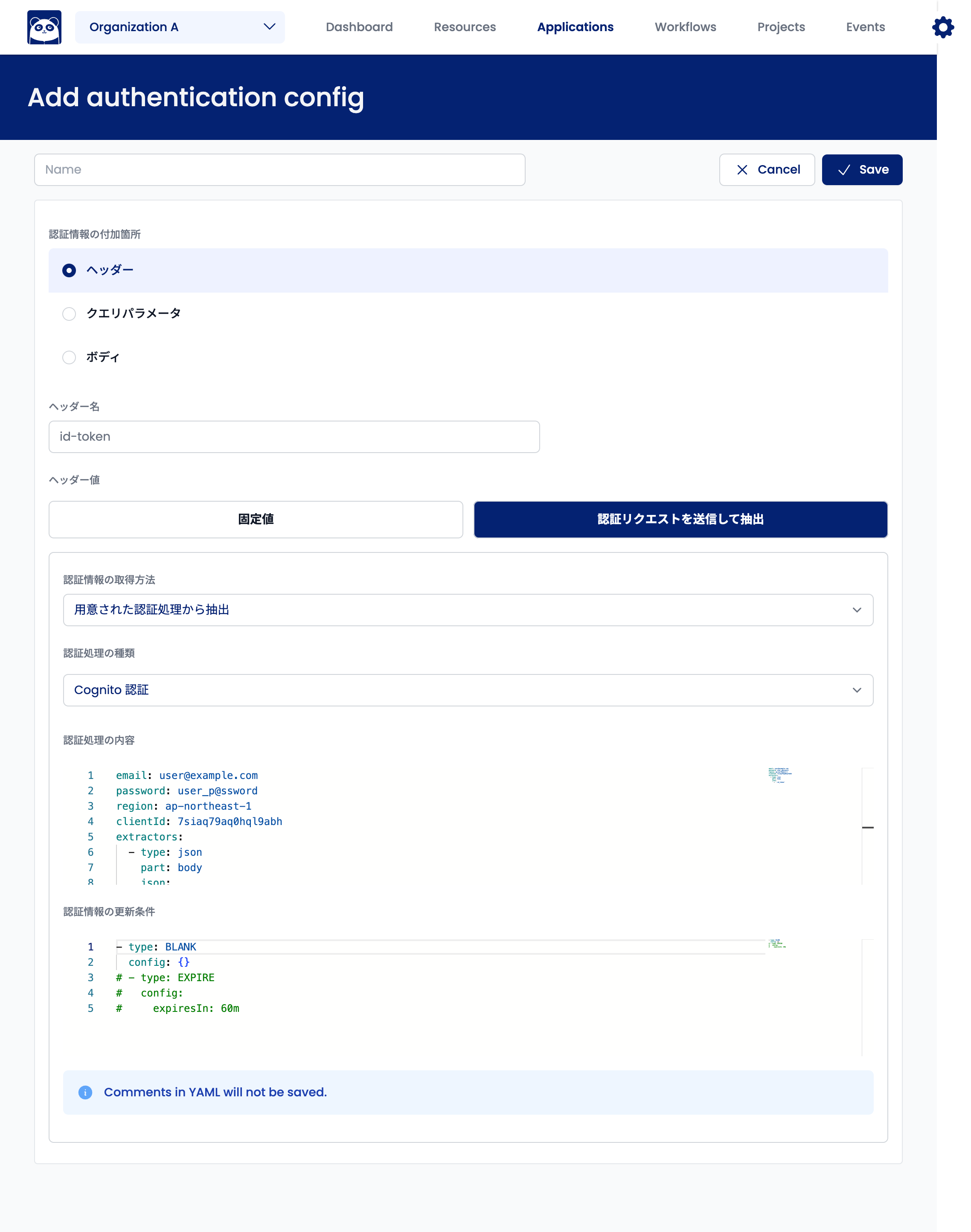
Select "Extract from Prepared Authentication Processing" for "Authentication Information Acquisition Method." Select "Cognito Authentication" for "Type of Authentication Processing."
For Cognito Authentication, "Authentication Processing Details" should include the following fields:
email: Login account's email addresspassword: Login passwordregion: AWS region codeclientId: Client ID issued by Cognitoextractors: Items of authentication information to extract
Example of "Authentication Processing Details":
email: user@example.com
password: user_p@ssword
region: ap-northeast-1
clientId: 7siaq79aq0hql9abh
extractors:
- type: json
part: body
json:
- ".id_token"
Specify json for type and body for part in extractors. The json field supports the following values:
.id_token.access_token.refresh_token.token_type.expires_in
You can only specify one value for the json field. You can only specify multiple extractors if a scenario follows the current one as post-processing. If post-processing is not set up, Shisho Cloud will extract the value set in extractors.
The "Authentication Information Update Conditions" setting is the same as when extracting authentication information from a scenario.
Extracting Authentication Information from Auth0
This authentication process connects to Auth0 to obtain ID tokens. Currently, only email and password authentication is supported. Custom domains for Auth0 authentication are not supported at this time.
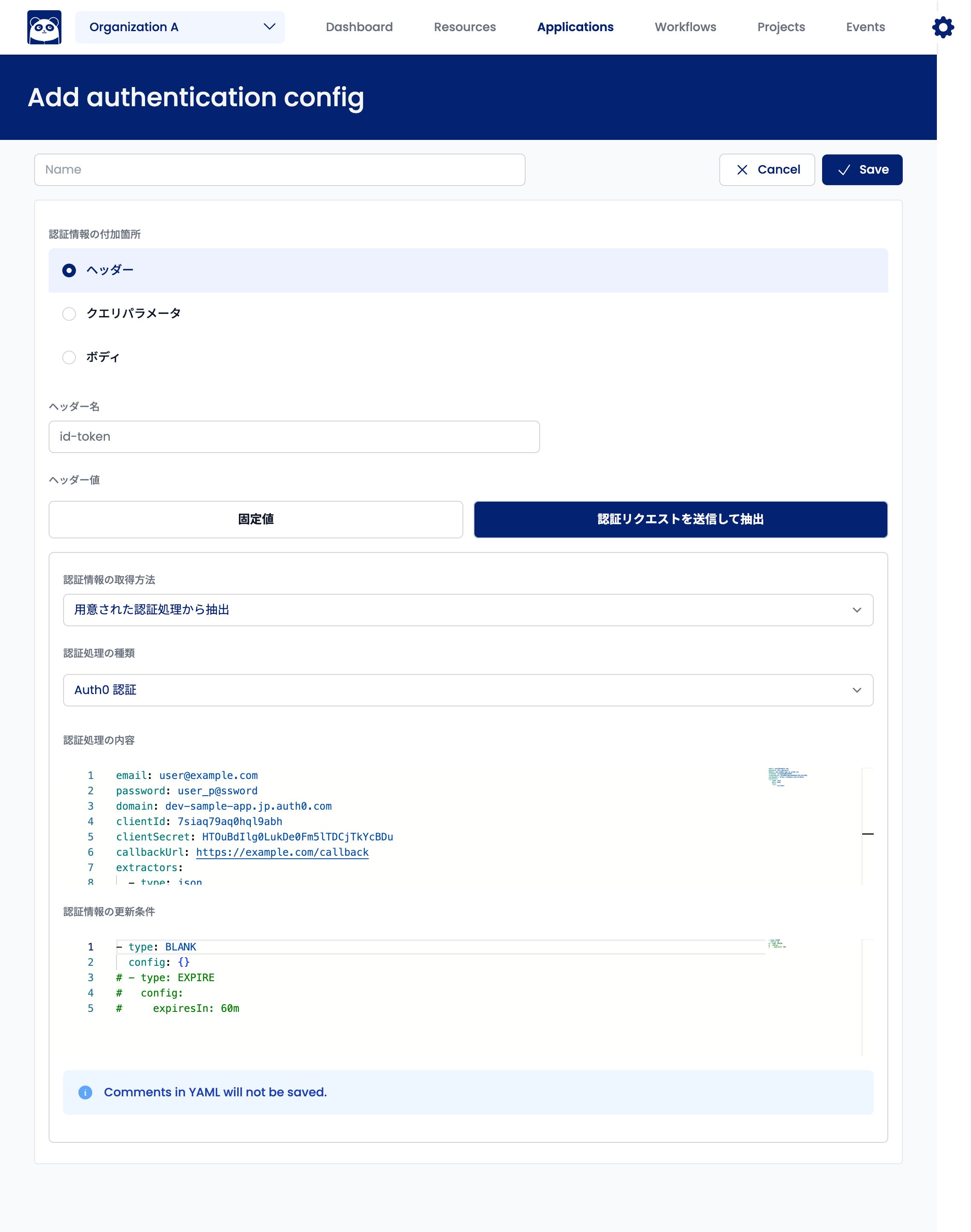
Select "Extract from Prepared Authentication Processing" for "Authentication Information Acquisition Method." Select "Auth0 Authentication" for "Type of Authentication Processing."
For Auth0 authentication, configure the following fields for "Authentication Processing Details":
email: Login account's email addresspassword: Login passworddomain: Authentication domain issued by Auth0 (subdomain ofauth0.com)clientId: Client ID issued by CognitoclientSecret: Client secret issued by CognitocallbackUrl: Callback URL allowed in the Cognito settingsextractors: Items of authentication information to extract
Example of "Authentication Processing Details":
email: user@example.com
password: user_p@ssword
domain: dev-sample-app.jp.auth0.com
clientId: 7siaq79aq0hql9abh
clientSecret: HTOuBdIlg0LukDe0Fm5lTDCjTkYcBDu
callbackUrl: https://example.com/callback
extractors:
- type: json
part: body
json:
- ".id_token"
Specify json for type and body for part in extractors. The following values can be specified for the json field:
.id_token.access_token.token_type.expires_in
You can only specify one value for the json field. You can specify multiple extractors only if a scenario follows the current one as post-processing. If no post-processing is set up, Shisho Cloud will extract the value set in extractors.
The "Authentication Information Update Condition" setting is the same as when extracting authentication information from a scenario.
Setting Up a Scenario as a Follow-Up Process for Prepared Authentication Processing
You can set up a scenario as a follow-up process for prepared authentication processing. This is suitable when an external authentication service, such as Firebase Authentication, receives a token and the application issues a session based on that token.
Select "Add scenario for post-processing to prepared authentication processing" for "Authentication Information Acquisition Method."
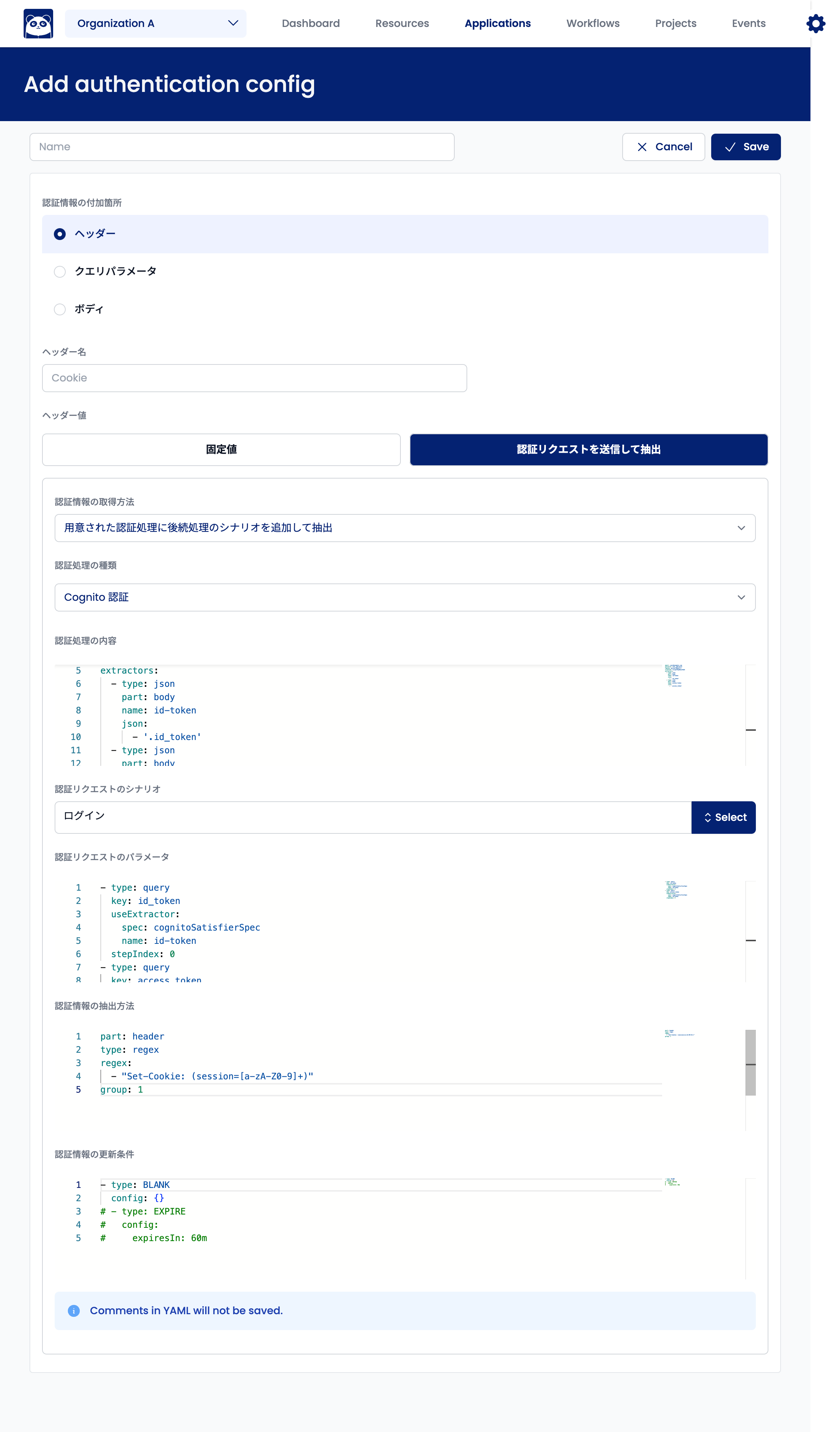
The above example will execute the "Login" scenario after Cognito authentication. The settings are the same as when setting up the prepared authentication processing and scenario independently. However, you need to change how you pass values from the prepared authentication processing results to the scenario.
First, add the name field to the prepared authentication processing's extractors. This name will be specified in the scenario input parameters. You can set multiple extractors when a scenario is set up for post-processing. In the following example, we add and specify name to pass the ID token and Access token to the scenario.
extractors:
- type: json
part: body
name: id-token
json:
- ".id_token"
- type: json
part: body
name: access-token
json:
- ".access_token"
Next, set "Authentication Request Parameters" to receive the value set in the above extractors. Specify useExtractor instead of value in "Authentication Request Parameters." In useExtractor, set the name field to the same name as the value you want to refer to in the extractors above. The example below shows how to reference the ID token and access token from the above extractors.
- type: query
key: id_token
useExtractor:
spec: cognitoSatisfierSpec
name: id-token
stepIndex: 0
- type: query
key: access_token
useExtractor:
spec: cognitoSatisfierSpec
name: id-token
stepIndex: 0
You must also set a field called spec in useExtractors. The value of this field depends on the type of prepared authentication processing used. Use the following values:
- Firebase authentication:
firebaseSatisfierSpec - Cognito authentication:
cognitoSatisfierSpec - Auth0 authentication:
auth0SatisfierSpec
This will execute the scenario after the prepared authentication processing. Authentication information will be extracted from the scenario based on the "Authentication Information Extraction Method" settings.
Setting Up Authentication Processing Consisting of Multiple Steps
Select the "YAML Editor" tab on the "Add Crawl/Assessment Authentication Settings" screen to configure authentication processing consisting of multiple steps with an order relationship.
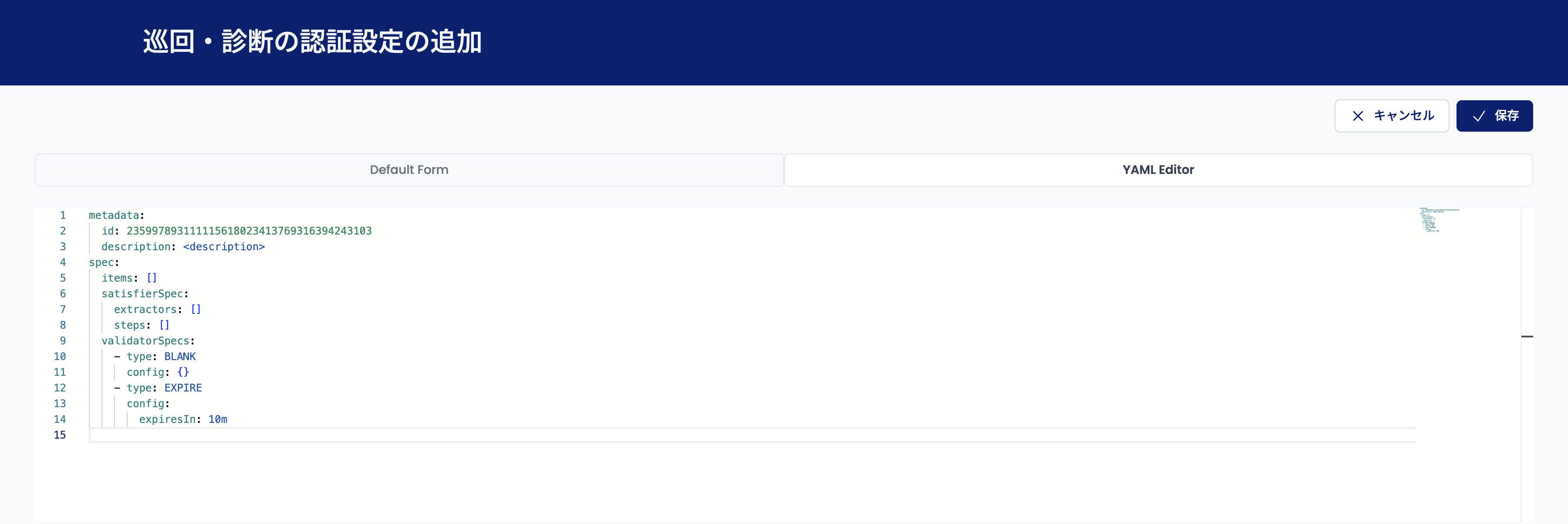
Use the editor to set the following items in YAML format:
metadata
Specify the authentication settings' metadata in metadata. Enter a description of the authentication settings in description. The list screen will display this as the title. The id is generated automatically, so there is no need to change it.
metadata:
id: 2359978...
description: "Authentication settings for cookies"
.spec.items
.spec.items defines the data managed by the authentication settings.
Specify the following fields in the object specified as an element of the field:
name: Authentication information nametype: The type of parameter injected by the authentication information (header,query, orbody)key: Key name of the parameter injected with the authentication information (e.g.,Cookie)value: Authentication information value- Set to an empty value unless statically set
Example:
items:
- name: cookie
type: header
key: Cookie
value: ""
.spec.satisfierSpec.steps
.spec.satisfierSpec.steps defines the authentication processing steps.
Use the following fields in the object specified as an element of the field:
type: Step typerequest: Sends a requestfirebase: Performs Firebase authenticationcognito: Performs Cognito authenticationauth0: Performs Auth0 authentication
spec: Specific step settings
The schema of the object specified in spec depends on the type specified by type.
Specify the following fields to configure the request details sent in that step if the type is request.
# HTTP method
method: GET
# Origin the request will be sent to (combination of scheme, host, and port)
origin: https://example.test
# Path to send the request to
path: /api/v1/
# Request headers
headers:
- key: Authorization
value: Bearer 123456789
# Query parameters
queries:
- key: id
value: 1
# Extractor settings for parameters to propagate between steps
extractors:
- { ... }
# Settings for using parameters extracted in one step in this step
bindings:
- { ... }
The extractors settings for propagating parameters are the same as those of the Extractor Object. The bindings settings are the same as those of bindings.
Specify the following fields to configure the authentication processing details in that step if the type is firebase, cognito, or auth0.
# Firebase authentication
email: test@example.test
password: testpassword
apiKey: testapikey
extractors:
- {...}
# Cognito authentication
email: test@example.test
password: testpassword
region: ap-northeast-1
clientId: testclientid
extractors:
- {...}
# Auth0 authentication
email: test@example.test
password: testpassword
domain: example.test
clientId: testclientid
clientSecret: testclientsecret
callbackUrl: https://example.test/callback
extractors:
- {...}
.spec.satisfierSpec.extractors
.spec.satisfierSpec.extractors configures the Extractor to run on the responses obtained in each step. The Extractor notation is the same as the Extractor Object.
Injecting Values Extracted by Extractor into an Item
The value extracted by each Extractor specified in .spec.satisfierSpec.steps[_].extractors and .spec.satisfierSpec.extractors will be injected into the authentication information. This is done when the Extractor name attribute value matches the authentication information name attribute value specified in items.
For example, the value extracted by the Extractor named cookie in the example below will be injected into the authentication information named cookie defined in items.
spec:
items:
- name: cookie
type: header
key: Cookie
value: ""
satisfierSpec:
steps: []
extractors:
- type: regex
part: header
group: 1
regex:
- "Set-Cookie: (SESSID=[a-zA-Z0-9]+)"
name: cookie
validatorSpecs:
- { ... }
.spec.validatorSpecs
.spec.validatorSpecs defines the conditions that trigger authentication setting updates.
This setting will already be configured, but you can change the expiresIn value to change the update interval. The value specified in this field should be interpretable as time.Duration in Go.
- type: BLANK
config: {}
- type: EXPIRE
config:
expiresIn: 10m